To achieve this speedup, Synopsys has announced that it is using NVIDIA CUDA-X libraries to optimise its solutions for next-generation semiconductor development. The company is also expanding support for the NVIDIA Grace CPU architecture and enabling more than 15 Synopsys solutions in 2025.
Commenting Sassine Ghazi, president and CEO of Synopsys said, "Synopsys technology is mission-critical to the productivity and capabilities of engineering teams from silicon to systems. By harnessing the performance of NVIDIA accelerated computing, we can help customers unlock new breakthroughs and deliver innovation even faster."
"Chip design is one of the most complex engineering challenges in human history," said Jensen Huang, founder and CEO of NVIDIA. "With NVIDIA Blackwell and CUDA-X, Synopsys is cutting simulation times from days to hours - advancing chip design to power the AI revolution."
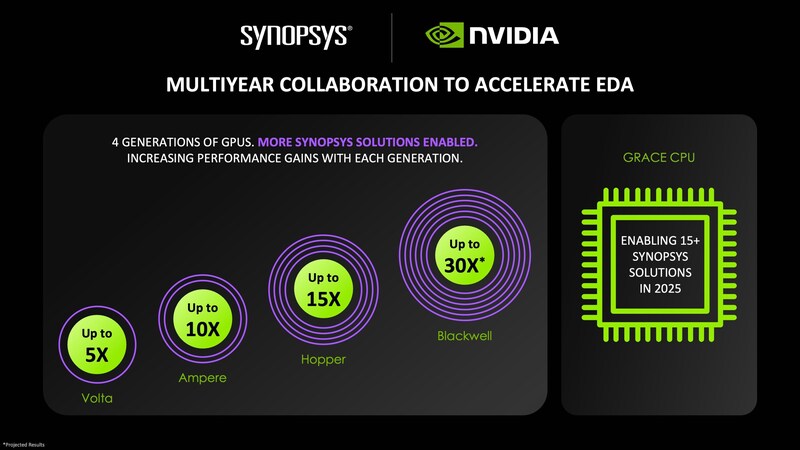
Synopsys and NVIDIA are advancing a multi-year collaborative effort to accelerate electronic design automation (EDA) workloads. Synopsys is applying NVIDIA accelerated compute architectures, including the NVIDIA GB200 Grace Blackwell Superchip, to achieve significant, projected runtime gains for workflows including circuit simulation, computational lithography, Technology Computer-Aided Design (TCAD), physical verification, and materials engineering.
These accelerated workflows include:
Circuit Simulation: Synopsys PrimeSim SPICE simulation workloads are projected to achieve a 30x speed up utilising the NVIDIA Grace Blackwell platform. At present, customers can achieve up to 15x speed with NVIDIA GH200 Superchips. NVIDIA accelerated computing architectures enable the simulation of challenging circuits to achieve signoff with SPICE-level accuracy, reducing runtimes from days to hours.
Computational Lithography: Synopsys Proteus provides optical proximity correction (OPC) software and inverse imaging technology (ILT) to resolve challenges at leading technology nodes. By leveraging NVIDIA technologies, Synopsys can deliver ‘game-changing’ technology to advance this computationally intensive manufacturing process. At present, Synopsys Proteus is optimised for NVIDIA H100 GPUs and integrated with the NVIDIA cuLitho library, achieving a 15x speed up of OPC. By leveraging the NVIDIA Blackwell platform, however Synopsys Proteus is expected to accelerate computational lithography simulations by up to 20x.
TCAD Simulation: Early results applying GPU-enabled capabilities and NVIDIA CUDA-X libraries to the Synopsys Sentauras TCAD process and device simulation solution is projected to accelerate time to results up to 10x. This solution is currently under development and is expected to be available to customers later this year.
Materials Engineering: Synopsys QuantumATK delivers atomic-scale modelling for semiconductor and materials research and development. Utilising CUDA-X libraries on the NVIDIA Hopper architecture can accelerate time to results up to 100x, enabling customers to simulate and analyse a wide range of materials with greater efficiency.
Synopsys said that it plans to continue enabling accelerated computing on NVIDIA platforms throughout its portfolio.
Synopsys and NVDIA's efforts to accelerate chip design also extend to speeding chip design with generative AI using NVIDIA NIM microservices.
For example, customers using Synopsys' Gen AI-powered knowledge assistant, Synopsys.ai Copilot, are seeing an average 2x productivity improvement compared to prior methods. The integration of NVIDIA NIM microservices is projected to enable an additional 2x speedup for even faster time to answers.
Additionally, Synopsys is enabling more than 15 solutions using the Grace CPU architecture for Synopsys EDA workloads spanning circuit simulation, physical verification, static timing analysis, and functional verification.
The company plans to further increase support on the Grace CPU architecture in 2025.













