With the growing demand for smart devices and wearable tech, and a strong focus on sustainability, this range of IP is increasingly important for chip design engineers.
As well as the fact that optimising power consumption has become a key concern, this IP is a significant consideration for several other reasons.
Firstly, power management IPs help to optimise the performance of electronic chips. These IPs can dynamically adjust voltage and frequency levels based on workload demands, so that the chip operates at the highest level while minimising power consumption. This approach improves system performance and responsiveness whilst regulating temperature.
Excessive heat can lower performance, reduce the lifespan of the IC and lead to system failures. Thermal issues can be avoided by controlling power usage and distributing heat more effectively to prevent overheating.
Power management IP is also critical for the reliability and longevity of electronic chips. Voltage fluctuations and power surges can cause premature system failures, and corrupted communication and data. These IPs provide voltage regulation and protection processes, preserving the stability of the entire system. As power management IPs can be tailored to specific application requirements, it’s possible for chip designers to optimise power efficiency based on the device's use case and performance demands. This flexibility enables the development of highly efficient solutions for a wide range of electronic devices.
Integration of power management functionalities allows for compact device designs and reduces the need for additional discrete components. This cuts manufacturing costs, reduces area, and simplifies product assembly. These IPs can also help chip designers to match the requirements of new power consumption and energy efficiency regulations, and to ensure electronic devices adhere to the relevant standards.
Overall, power management IPs are crucial for maximising energy efficiency, enhancing device performance and meeting the evolving demands of modern electronic systems.
Power Management IP Components
Typical functions used in power management include low drop-out (LDO) linear voltage regulators, voltage references and power-on-reset (POR) circuits. These components are commonly combined into a dedicated power management unit (PMU) that supplies all of the sub-blocks. The power management blocks are analogue and mixed- signal circuits specialised for the application. Each of these blocks can be optimised for a specific application to achieve significant improvement in power, and a reduction in system cost.
LDOs are widely used to provide an accurate, low noise, regulated, voltage level from a battery, or other source, at the expense of a minimum voltage drop (or dropout voltage). In a typical LDO a dropout of 100 to 200mV gives sufficient headroom to filter the incoming supply to provide line and load regulation, creating a low noise and stable output voltage against power supply and load variations.
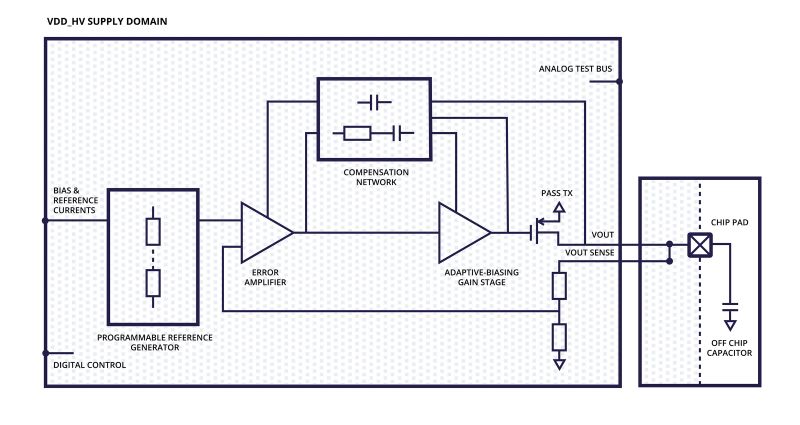
LDOs provide an accurate, low noise, regulated voltage level from a battery or other source
Voltage and current references provide accurate stable references that are used by other components within the system. These are essential for accurate measurement and control of any digital circuit, including LDOs. The main purpose of a voltage reference is to provide a constant known value over process, voltage, and temperature (PVT) variation. Low power consumption and good power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) are part of a high- performance and reliable reference voltage. Voltage references typically exploit the inherent bandgap energy of silicon. The bandgap utilises two voltages with opposite temperature coefficients (the base-emitter voltage, and the voltage across a resistor) to produce a temperature independent reference.
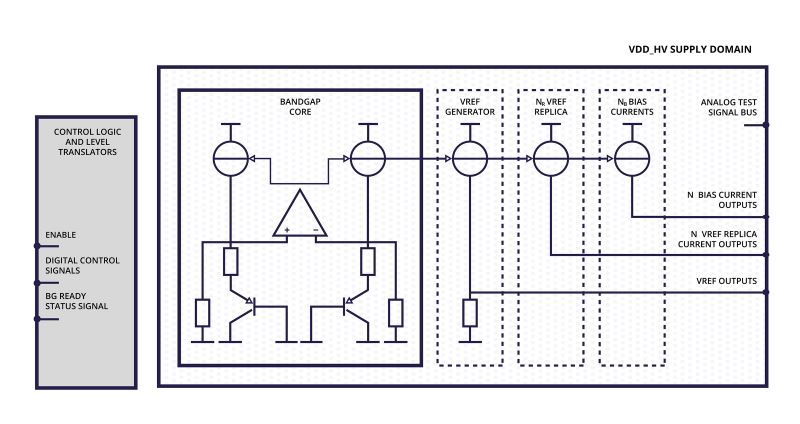
The bandgap utilises two voltages with opposite temperature co-efficiencies to produce a temperature independent reference
Power-on-reset circuits are an important element of many ASIC/SoC designs, to hold off the start-up of logic circuits until the power supply voltages have reached an adequate level to achieve valid logic states in the system. These can prevent unexpected system behaviour and protect sensitive components from damage during power-up or power-down sequences.
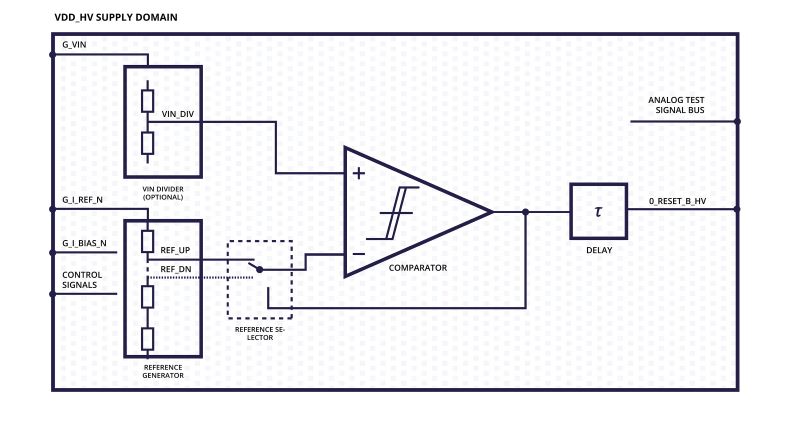
Power-on-rset can prevent unexpected system behaviours and protect sensitive components from damage
The use of these power management blocks on an ASIC/SoC is generally not independent. Frequently, systems require very carefully controlled power-up and power-down sequencing of the various supply rails and the ability to shut down certain power supplies during specified low-power operating states of the ASIC/SoC. To control the different power management blocks, a logic state machine can be added to ensure the right timing and sequencing of power supply bring-up and shut-down, as well as to establish the various low-power states.
Power Management IP Challenges
Chip design engineers face many different challenges when dealing with traditional power management IP solutions. Designing and implementing power management IPs can be difficult, requiring a deep understanding of analogue and mixed-signal circuit design techniques.
Integrating these IPs into existing systems or designs may present problems related to compatibility, interface protocols and system integration, while balancing power efficiency with performance and functionality may mean there are compromises, where optimising one aspect may impact negatively on others.
Validating and testing power management IPs is often time-consuming and resource intensive. Power management IP can add to the overall cost and area of an electronic system. Careful consideration must be given to the trade-offs between cost, performance, and features when selecting and implementing power management solutions. This is particularly true in advanced nodes where, due to limited analogue scaling, and high wafer costs, the decision between on and off chip power management is complex.
Trends and Opportunities
Power management IP is constantly evolving, with new technologies and techniques emerging to address the challenges and opportunities presented by the need for more energy-efficient and high-performance electronic devices. This IP is increasingly being integrated with other system components, such as microcontrollers and SoCs, to provide effective solutions.
Continued advances in analogue and mixed-signal design techniques will enable the development of more efficient and reliable power management circuits.
As the global focus on sustainability grows, there will be even greater demand for energy-efficient electronic devices, driving innovation in power management IP. It means that this IP will continue to play a critical role in enabling new applications, such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, smart wearable tech, high performance computing (HPC), and autonomous vehicles.
It’s clear that power management IP is a crucial component of modern electronic systems, providing essential functions such as voltage regulation, power-on-reset, and thermal management.
Agile Analog is well placed to offer highly configurable power management IP that is available on any process, for any foundry. This digitally wrapped and verified IP can be integrated seamlessly by chip designers into any SoC, significantly reducing complexity, costs and time.
As the popularity of electronic devices continues to surge, the importance of power management IP will only increase. By staying up-to-date with the latest advances, chip designers can develop products that meet the changing needs of consumers while minimising the environmental impact.
Author details: Chris Morrison, Director of Product Marketing, Agile Analog













